A Healthy Mouth for a Healthy Body
Gum Diseases and Systemic Inflamation - A Healthy Mouth For a Healthy Body
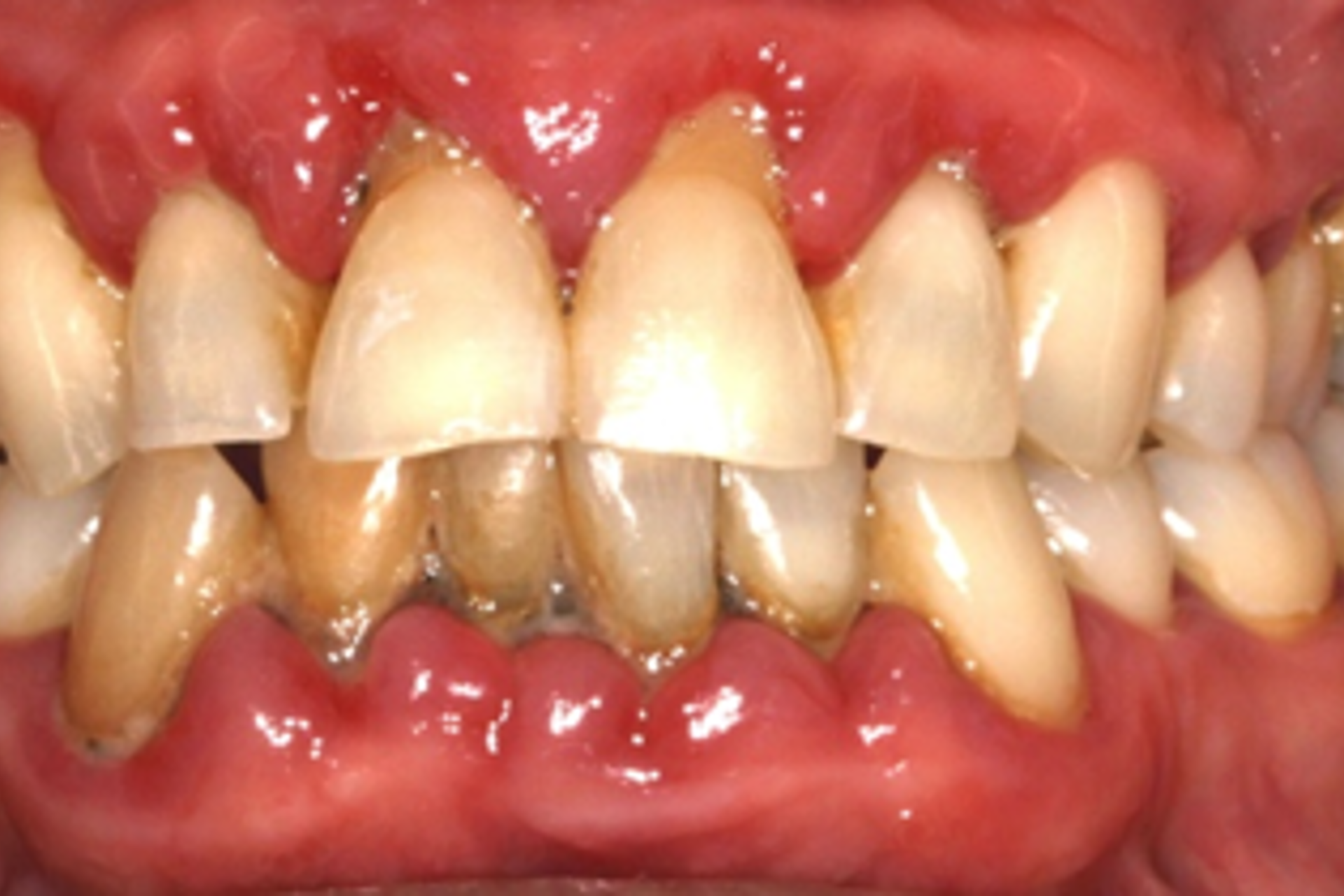
The term “Periodontal Medicine” refers to a branch of periodontology focussing on how periodontal health and disease and systemic health and disease are inter-related. These relationships are based on the understanding that gum inflammation (arising from gum infection) is a significant source of overall chronic inflammatory load at the whole-body level. We know that inflammation is a very significant component of many chronic diseases including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis. Current evidence suggests that individuals with periodontal inflammation may also be susceptible to other such diseases that have as a hallmark feature “inflammation”.
Systemic diseases/conditions associated with periodontitis:
- Diabetes
- Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes
- Cardiovascular disease
- Pulmonary disease
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Obesity
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Oral Cancer
It is important to note this does not suggest that periodontal disease causes any of these conditions but rather that periodontal infection and inflammation may be associated with the clinical manifestation of these conditions and may influence the severity of these conditions. Periodontal medicine allows us to consider periodontitis and systemic conditions as “two-way” relationships in which periodontitis can affect systemic health but also that systemic health can affect periodontitis. It is recommended that individuals diagnosed with inflammatory conditions undergo a periodontal examination and if active periodontal disease is detected this should be managed as part of an overall health protocol to reduce the systemic burden of inflammation.
